What is a Distribution Strategy? Importance of Distribution Strategy
Did you know that sales are the key to higher revenues and contented workers? That’s true, and if you want to sell more, you should make a plan. First, you should have a goal to attract and retain customers. Second, you should deliver a product or service to the customer and the correct information. To achieve this, you should come up with a distribution strategy that goes well with your business needs. This strategy will help you manage the complete sales process. But, do you know what it is all about? If not, don’t worry; this guide will educate you.

Table of Contents
- What is a Distribution Strategy?
- How to select the right Distribution Strategy
- Distribution Strategy: Stay competitive in the Digital world
- Distribution Strategy examples
- What are different types of Distribution Strategy?
- What are different distribution Channels?
- How can I select the right distribution strategy for my wholesale business?
- Key Modules of the Distribution Software
- What is the difference between Direct and Indirect Distribution
- Conclusion
What is a Distribution Strategy?
In a nutshell, the best distribution strategy definition is a plan to help you deliver a product or a service to the customers you are targeting via a supply chain. This plan includes all the approaches you would use to give the customers what they expect from you. A good strategy can incorporate your distribution channels or employ other companies’ channels. In addition, your business can use its exclusive stores or sell through other retail stores.
Moreover, a business can use both its stores and third-party retail chains. In modern times, especially after the Covid-19 epidemic, companies are using online exclusive sales channels. Hence, you should pick a distribution channel strategy that suits your business. The best approach will help you deliver goods or services to the target audience at optimal distribution costs. It will also maximize your sales revenues and profits. On the other hand, Bad distribution strategy types will cause losses and let your competitors win.
How to select the right Distribution Strategy
Now you know what a distribution strategy is. Next, you will learn how to select the right one for your business. There are a few factors to reflect on, and they include:
Check the market status right now
Before coming up with a distribution marketing strategy, carry out a thorough market analysis. The goal is to discover the correct way to distribute the type of products you sell. For instance, if you deal with consumer goods, the proper technique is FMCG distribution. Only a meticulous market analysis can reveal the appropriate distribution channels for your products. It can also help you study customers’ buying behavior and pinpoint their specific needs.
Distribution costs
No matter the channel you choose, there will be costs to incur. If you select a more comprehensive direct distribution strategy, it means you will sell directly to the final customer. The method is more straightforward, but it has some costs to incur. The more comprehensive strategy involving intermediaries is more convenient, and goods can reach customers almost immediately. However, every intermediary should earn something to continue being loyal to you. In essence, you should develop charts and graphs showing potential costs and profits from each distribution channel.
Do you sell complex or simple products?
As you try to create a sales distribution strategy, focus on your product. The product is complex in that it requires technical support after delivery. Do the customers need an after-sale service, such as installation and maintenance help? If so, you should sell it more directly to go to a dealer and then to a customer. The dealer will help your customers sort out their issues. On the other hand, if your product is a typical household appliance, such as a blender, you can select an extended distribution channel for it.
What profits are you targeting?
If you choose the shortest distribution method, your business revenues can increase. Nonetheless, this can happen only if you don’t sell FMCG products. For these, you need a more extended distribution channel to increase your revenues and profits. In some situations, higher revenues may not translate to higher net profits.
What will be your market share?
How quickly can your business establish itself in a new market? If such a market is already saturated, you will find it hard to penetrate a new market. There will be competitors doing well already, and it will take longer to get a market share. So you have to do you distribute strategy math very carefully.
Where your product is in its life cycle
If your product is new, a more extended distribution channel is necessary to ensure it is recognized on the market. As you choose who to connect and grow with, you should consider their availability and expertise.
Distribution Strategy: Stay competitive in the Digital World
As you think of how to make a distribution strategy, focus on technology. First, think of how to use technology to promote and sell your products. In this case, you should explore eCommerce as a distribution channel. It is estimated that by 2021, e-commerce sales will reach 4.8 trillion. Why wouldn’t you want to be part of that? Countless people are using apps to buy things online, and you can sell to them too. Secondly, you can use technology to implement your preferred distribution strategy. As you will learn below, there is software that can help you manage your supply chain processes
Distribution Strategy examples.
A suitable distribution strategy example will vary depending on the marketing channels you have selected. First, a direct channel occurs when a manufacturer sells straight to the consumer. The channel must be short if it’s direct. Hence, good examples of this are primarily retail brands that sell fast foods and perishable goods.
An indirect marketing channel, it occurs when the path is long and complex. Typically, there will be many distributors and middlemen. Examples can be soft drinks companies, including Coca-Cola and Pepsi
An intensive distribution strategy is more intensive and considers more than just the size of a distribution channel. It uses a more aggressive approach, and examples include vehicle brands and distributors of household appliances.
Moreover, a business can use an exclusive strategy when it has a high brand value to protect. It will open stores in major cities with upper-income and classy customers and still outdo its competitors. Examples are big fashion houses with high-end designer products.
Lastly, some businesses use a selective distribution strategy. You will find them on almost every street, or they may start a few stores in every major town. Good examples are big supermarkets and retail chains.

What are the different types of Distribution strategy?
Direct distribution
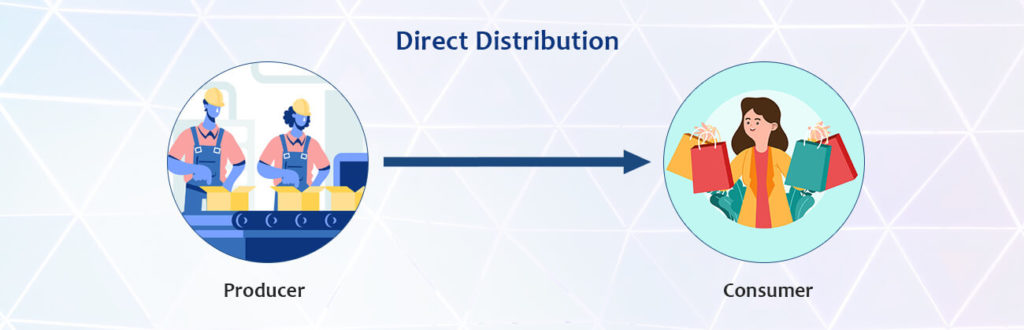
Here, manufacturers sell directly to the end consumer. Some direct distributors sell online, particularly those targeting younger generations that have more technological knowledge. The rest use product catalogs, product lists, phone calls, and other advertising methods.
Indirect distribution
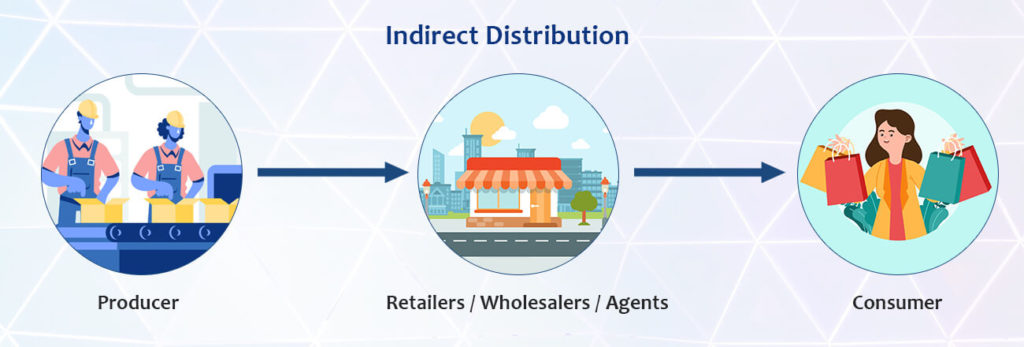
It is the opposite of the direct distribution method. Simply, this method entails intermediaries like wholesalers, retailers, and agents.
Intensive distribution
As aforementioned, this technique entails a more aggressive and extensive marketing approach. Hence, several retail outlets are opened to reach more customers and increase sales revenues and profits.
Exclusive distribution strategy
This method is a preference of companies that sell luxury goods. To purchase their products, you must approach their dealership. A good example here can be the Mercedes Benz car brand.
Selective Distribution
This technique is partly similar to intensive and exclusive strategies. Those who use this technique know full well that not all people will be interested in their products. So they set up stores in some selected areas. Their stores don’t sell anything else, and if they pick external stores, these will sell closely related products.
Related articles
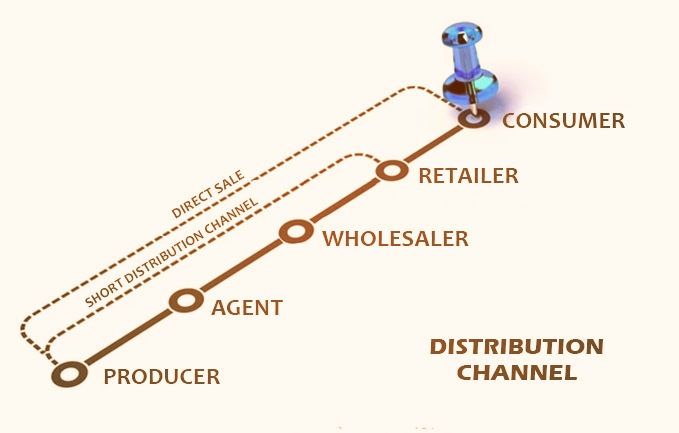
What are different distribution Channels?
These channels are all about how to distribute products to customers. As a distributor, you obtain goods, store them, and then sell them to customers via a distribution channel. Different channels include the following levels:
- Zero – This distribution channel involves direct contact between manufacturers and customers. It is the shortest.
- One – This one entails one middleman standing between the manufacturer and the consumer.
- Two – It involves two intermediaries, and this can be a wholesaler and a retailer.
- Three – This distribution channel has three middlemen, namely: agent, wholesaler, and retailer.
How can I select the right distribution strategy for my wholesale business?
If you are a wholesaler, you need a product distribution strategy that works for your business. There are different types of systems, but some may not work for your business. The system that might work for you might not help the next wholesaler. You can opt for direct marketing via telemarketing and product catalogs or choose eCommerce marketing. It can be trial and error at first, but eventually, you will discover the best strategy for your business. Briefly, you should:
Know your customers perfectly
Ensure you find out who your target customers are, what they need from you, how soon they want it delivered, and where
Focus on your product
If you sell perishable goods or daily-use products, by all means, choose a direct channel. On the other hand, if you deal with non-perishable goods, choose indirect marketing channels. More to the point, select your intermediaries wisely.
Seek professional help
As a wholesaler in any industry, you have competitors. Any small error in decision-making can cost your business considerable losses in terms of time and money. Thus, if you honestly can’t select the right distribution strategy alone, find a professional who can help you.
After finding a distribution strategy to get the message to customers, the next thing is to implement it. As technology has become more innovative than ever, you should use it in your business. More specifically, you should start searching for the best distribution software. It would be best if you bought wholesaler distribution software as it is designed for your business. Not only will it make the distribution process easier to track, but it can also reduce human errors and stress.
A good software tool for distributors should have automation capabilities. In other words, it should boost productivity and ensure that you complete tasks quickly. Another component of this software is RFID tracking which simplifies inventory monitoring in real-time. It is based on a modern technology called the Internet of Things. Moreover, the software needs to have all business management modules in a central position. The most common modules are accounting, warehousing management, customer relationships management, inventory management, and procurement management. Lastly, the software should be cloud-based rather than in-house. Cloud-based distribution software is easy to access from any place, anytime, as long as there is a Wi-Fi hotspot and mobile gadget.
Key Modules of the Distribution Software
Distribution software includes modules to manage plan, administer, execute, track, and report the tasks running in Distribution warehouses that belong to wholesale distributors business. Distribution software contains the ‘Flow’ of material for distributors. Key Features of the Distribution Software are:
- Sales Order Management
- CRM
- Inventory Management
- E-Commerce
- Product Catalog
- Employee Management
- Billing
What is the difference between Direct and Indirect Distribution?
In direct distribution, the product is distributed to the end-user from the manufacturer’s or distributor’s warehouse. This is usually the case for a manufacturer that sells its items via a distribution center or retail outlet. In indirect distribution, the product (i.e. a service) is provided through a supplier or agent who’s contractually obligated through the manufacturer to buy the products and supply them to the end-user. The indirect distribution technique is regularly used by manufacturers and distributors to make certain they don’t oversell or have leftover products.
Direct Distribution = Direct-to-consumer (DTC) is a distribution channel that is not utilized by the brand. The main reason for the use of this channel is to gain a competitive benefit as it is a quicker and more direct way to reach the customer. Companies use direct distribution channels for customer products as it is very effective. This is a direct method of reaching the consumer with the product.
Indirect distribution is an indirect form of distribution channel and is used to sell products and services. It is also called indirect marketing. It is a form of marketing that involves a company or individual taking someone else to make a sale for them. This is known as indirect distribution as it does not involve the company or individual going to the customer directly.
FAQ about Distribution Strategy?
1. What are the 4 types of distribution strategy?
First, a distribution strategy is a plan for distributing goods or services to customers. Successful distribution of your product or service will depend on your selling strategy. There are four distribution strategies, and they include the following:
- Direct – A manufacturer uses a direct distribution method when they want to avoid intermediaries. They can create an eCommerce website and sell their item to direct online customers. Alternatively, they can use catalogs or sell directly via phone calls. The best-selling method for a company depends on the customers’ technical knowledge and age.
- Indirect – This technique includes an intermediary that delivers goods to the customer. Thus, an indirect marketing channel is longer than a direct one. A company will consider the type of items it produces and the customers it wants to reach. An indirect distribution technique can include wholesalers who take goods directly from the manufacturer. After that, they sell these goods to retailers who distribute them in small quantities.
- Intensive – A manufacturer chooses many retail shops to which they deliver their product. An Intensive distribution method suits items like candy or biscuits. These snacks sell fast regardless of the location or shop type. As customers buy these snacks on impulse, the intensive distribution technique tends to work best.
- Selective – It includes Intensive and Exclusive distribution techniques. An Exclusive distribution strategy involves just one point of sale, such as a retail store. The manufacturer creates branded stores and puts them in different locations. So the only way to get their product is to visit the branded store. This technique works for luxury products like high-end vehicles. A Selective distribution method has the traits of Intensive and Exclusive strategies since the manufacturer places products in its branded stores and a few departmental stores.
2. What are the critical parts of a Distribution Strategy?
A distribution strategy has six parts or elements. These include:
- Order processing
- Customer service
- Transportation method
- Inventory control
- Materials handling
- Warehousing.
3. How do you determine a distribution Strategy?
Selecting the correct distribution method determines your overall selling success. So, it is necessary to understand the tastes and preferences of your target consumer. For instance, younger generations have more technical knowledge while older generations may prefer simplicity.
Customer perception of your brand matters a lot when selecting a distribution channel. If they view it as a luxury brand, you might choose an Exclusive or Selective distribution strategy.
A pricing strategy that works for the chosen distribution channel is a must to ensure everyone involved benefits from the deal. Lastly, the relationship you share with your customers is a vital consideration.
Best way to send your goods to the customers
Companies produce different items, meaning their distribution strategies cannot be similar. When selecting the best way to send your goods to the customers, reflect on the following:
- Who is your competition, and how do they distribute their goods? If there is a distribution technique that none of them or only a few of them use, you can grab it. For instance, some of your competitors may not yet have an eCommerce website. Those who have a website may not be actively promoting it to get leads. You can fill this gap and make more significant profits.
- Cost of using a given distribution channel – Choosing the best distribution strategy is not enough. You must incur some charges for building a reliable support system. Can you handle these expenses with your current financial resources?
- Create your favorite list of options – So far, you have examined different distribution methods based on their pros and cons. Next, make a list of options starting with the most beneficial approach. Finally, select the strategy that could get you many customers.
- Create an expansion plan – As your business grows, you might have to select more distribution channels. To do that well, study the market to know what your target audience wants and how you can send it to them. Also, consider the new techniques your competitors adopt.
4. Why is a distribution strategy important?
Selecting the best distribution strategy is necessary because of various reasons. Some of them include:
- You can ship your products to the target markets without causing unnecessary delays.
- Knowing the best distribution method can help you improve customer experience. It can provide information on consumer preferences and tastes and help you fulfill their needs.
- An accessible, intuitive, affordable distribution channel can help build and retain customer loyalty. You can deliver the items your customers want on time.
- The best distribution channel can let you find ways to deliver goods cheaply. For instance, you can outsource the transportation and logistics role to an able distributor.
- Choosing a perfect distribution strategy can let your company reach its long-term goals to ensure faster growth and higher revenues.
5. How does technology enable distribution strategy execution?
Technology growth affects distribution execution in some ways. It makes the distribution role better in the following ways:
- There are new software systems that improve information flow via the automation of different areas of the supply chain. For instance, a distribution enterprise resource planning (ERP) tool puts all the necessary logistics disciplines into a single centralized database.
- Automation of distribution networks keeps every supply chain participant informed. For instance, distributors can track their inventories in real-time and instantly tell their suppliers or manufacturers so they can adjust their production cycles and quantities based on current demand.
- Technology has led to the release of new warehouse management machines. These reduce human labor and its errors. Warehouses do not have to be large buildings now. With pallets, conveyor belts, elevators, and rail systems that receive control commands from a central computer network, warehousing is an easier task.
- Software technology allows traffic managers to choose the most cost-effective loading and delivery systems. GPS systems show drivers the least expensive and the most secure routes. Technology will keep shifting to help shorten delivery times, improve the safety of goods in transit, and lower the cost of inventory management.
Conclusion
If you want to create an effective distribution strategy, you should know that this is a multi-faceted and complex process. You have up to five distribution channels to choose from and a range of factors to think about. Whether you settle on a direct, indirect, intensive, exclusive, or selective marketing strategy, you need software to simplify the implementation process. In addition, if you cannot develop a strategy alone, you can consult a professional.
Related articles
- What is ERP? | How It Can Help Your Business Grow
- How to Choose an ERP Consultant?
- 6 Key Benefits of ERP Accounting System
- Best Purchase Management ERP | Top Order ERP Systems
- 8 Features that Describe the Importance of ERP for Business
- What is Cloud ERP and How Does It Work? | Advantages of Cloud ERP
Posted on
ERP vs CRM: What is the difference?

What is ERP?
We will describe the differences between ERP vs CRM before defining ERP and CRM. ERP or Enterprise Resource Planning is a software system consisting of different business management modules. ERP vs CRM is used to increase profitability. You can think of it as one extensive database comprising financial management, accounting, purchase management, human capital management, Customer relationship management, project management, warehouse management, business intelligence, and sales management, among other modules. A business selects the modules to add to the ERP software to boost productivity, profitability, and efficiency.
Table of Contents
- What is CRM?
- Key difference between ERP vs CRM
- ERP vs CRM – Key Features
- ERP vs CRM: Key Benefits
- CRM vs Cloud ERP
- How are ERP and CRM systems similar?
- Can CRM be integrated with ERP?
- Is CRM part of ERP?
- Integration of CRM, SCM, and ERP
- Does our Distribution business need ERP or CRM, or Both?
- Cloud CRM vs Cloud ERP
- Conclusion
What is CRM?
CRM refers to Customer Relationship Management. It is a type of software program that businesses use to scrutinize and manage customer interactions and data all over a customer lifecycle. They use this tool to enhance customer service relationships. A CRM software program can collect customers’ data across various contact points between a business and a customer. Concerning ERP vs CRM, all business departments require ERP, while the sales and marketing team mainly needs?CRM. Each communication between a business and a customer enters into the CRM database for future retrieval. Besides capturing details of every customer, A CRM program can help a business design or identify the most desirable products and services.

See How We Can Help to Reduce Your Operational Costs for Your Wholesale Distribution Business.
Ximple ERP automation improves workflows & processes across the distribution departments which help to reduce operational cost and productivity.
If you want our wholsale distribution business experts at Ximple Solution to help you digitalize your distribution business or upgrade your legacy ERP, just book a call

The key difference between ERP vs CRM
After defining ERP vs CRM, next, we will describe the differences between ERP software vs CRM. These two are essential business management software tools but are they different? ERP vs CRM is used to increase profitability. ERP vs CRM integration so crucial The following are the main differences between them:
- While ERP controls different business functions, CRM provides a single database for the sales function or department.
- It is easier to install CRM as it is a single system targeting the sales process and team. On the other hand, it isn’t easy to implement ERP because it can have several modules as a business requires.
- CRM being sales-specific software, shifting customer data to it is more straightforward. On the other hand, transferring the entire organization’s data from previously owned automated solutions to the ERP system is laborious.
- An ERP purchase and implementation process demands a more substantial financial commitment than a CRM purchase and execution.
- When it comes to who needs ERP and CRM, it is clear that a few medium-sized enterprises and many large-scale businesses can afford the expensive ERP. On the other hand, almost all small businesses would struggle to implement the costly ERP. They can easily afford CRM implementation.
Key Features: ERP vs CRM
An ERP system can have as many functions and modules as a client wants. However, some of these are critical and commonly included during ERP implementation. Features of an ERP vs CRM are more holistic in terms of the business as a whole. As you will see in the functions indexed below.
Common ERP Features
- Finance and Accounting
- Procurement or purchasing
- Manufacturing
- Inventory management
- Order management
- Warehouse management
- Supply chain management
- Customer relationship management
- Project management
- Human capital management
- Service Resource Management
- E-commerce
- Sales and Marketing Management
As you can see, you should not confuse ERP vs CRM software because CRM can be a part of ERP.
Common CRM Features
A single Customer Relationship Management program can have as many as 30 features. All businesses don’t need all of these features. The most important and common ones are:
- Contact management – Enables a business to create a big customer contacts list and use it for marketing later on.
- Lead management – It’s not every customer that is worth following up. With this module, you can sort high-quality leads and strive to retain them.
- Lead scoring module – This is a crucial feature that can help a sales team identify leads likely to convert to loyal customers.
- Sales analytics – This module is vital as it can help the sales team gather data from all platforms, analyze it, and create analytical reports to be used when creating future sales campaigns.
- Mobile CRM – This feature ensures that CRM is available to mobile device salespeople.
- Sales forecasting – This is a feature that will help the sales department create a yardstick to measure sales efforts against the actual results.
- Salesforce Automation – This is a tool for automating routine tasks that employees do to help them focus on other more beneficial tasks.
- Emails Client Integration – This is all about having an email client within the CRM software for more accessible communication.
- Business intelligence, reporting, and dashboards – allow users to capture real-time data updates no matter the platform they are using. As a result, they can make better decisions.
- Data or file storage – This feature is created in CRM software systems to help users store and retrieve data quickly.
- File Sync and Share feature – You can merge CRM with Google Drive, DropBox, Outlook, MS Excel spreadsheets, or any other program you like.
- Sales Performance Management – This module is added to help management overview the sales team’s performance.
ERP vs CRM: Key Benefits
These ERP and CRM systems have several benefits in the way they help manage company processes.
Let’s take a look at ERP vs CRM benefits:
Benefits of ERP
By implementing ERP, a company can note some advantages. These are:
- An ERP system provides a module for each department, helping the whole organization work as a team.
- Although the initial cost of executing ERP is high, the system fully recovers it in the future by reducing overheads and streamlining processes.
- ERP automates business functions and gets rid of paper-based operations.
- ERP improves decision-making processes among seniors and subordinates by generating real-time data.
- ERP improves stock management by assigning a barcode to each element of a finished product. The same barcode gives potential customers more information about the product itself.
Benefits of CRM Cloud
A cloud CRM is a customer relationship software program that exists in the cloud. Therefore you can access it anytime as long as you have an internet connection and a browser. ERP or CRM can be on the cloud; it is your choice. Advantages of using a CRM cloud system include:
- It is super easy to install CRM software even if you are a small business.
- Cloud CRM is a seamless system that a salesperson can access from any place any time they like.
- Although your sales team needs training, the whole onboarding process is more straightforward than that of ERP.
- CRM cloud can help a business save time, one of the most irreplaceable resources.
- ERP CRM solutions encourage teamwork and collaboration as everyone must refer to a central database.
- Cloud CRM software is scalable and versatile, meaning that it will still fit your business if it expands.
- CRM that is in the cloud can be combined with other essential business applications to simplify the sales team’s work.
- It includes constant updates and provides reliable data backup.
CRM vs Cloud ERP
When deciding between CRM vs ERP applications, it can be easy to determine the one you want based on if it is in the cloud or not. First, if you can afford to install cloud ERP, then do it and ensure that you include a CRM module. A standalone CRM is fine, but it cannot compare to an ERP already in the cloud in terms of benefits.
Your sales team can access this type of CRM at the office only. This is not the case for a team that is using Cloud ERP with a CRM module. They will always access it no matter where they are as long you have an active Wi-Fi hotspot.
How are ERP and CRM systems similar?
In this section, we want to describe the similarities between the ERP & CRM systems. Are they even related to each other? The answer is yes. The main similarity between the systems is that CRM is a common component of ERP. While a separate CRM module in a whole ERP system can’t be as robust as a standalone CRM software tool, it still works. It will generally lack some standard features found in a standalone CRM system. If present, the features might be brief.
Can CRM be integrated with ERP?
Yes, ERP and CRM integration is possible. This can allow you to have a single software system that can manage every other business process plus sales. What we mean by integration is that standalone CRM software is connected to an ERP to ensure that they work together as one system.
Is CRM part of ERP?
Customer Relationship Management is a unique business function that deals with sales activities. As software, CRM can stand alone or be merged with ERP. When integrated with ERP, CRM is one of the five most important features of an Enterprise Resource planning system.
Integration of CRM, SCM, and ERP
So far, you understand the meaning of ERP and CRM. When these are combined with SCM, do they even work? SCM refers to Supply Chain Management. This is a critical business function, especially for distributors and wholesalers. It is possible to have ERP systems that have a Customer Relationship Management module and a Supply Chain Management module. Each component will enhance your employee’s work. You can hire an ERP CRM SCM software company to help you carry out the complicated integration task.
Does our Distribution business need ERP or CRM, or Both?
As a distributor, you want activities per distribution channel to be quick and error-free. You can do so by obtaining CRM software. This can be a separate tool, or it can be a part of your ERP. If you already have distributor ERP software, the easiest way to have CRM is to add it as a module. If you don’t have ERP and cannot afford it right now, you may be best buying the CRM software alone.
The choice to invest in a CRM, ERP, or both will depend on the requirement of your company. A business with a small number of high-value customers and complex financials should invest in ERP Software.
You don’t need both software systems if you have a customizable ERP and your sales function is manageable. However, if you run a large business with global networks, your sales activities might require a Standalone CRM software program for robust management. If you cannot afford either, there are ERP CRM open source tools for you.
Cloud CRM vs Cloud ERP
When making ERP CRM cloud decisions, you have to be careful. Will you deploy ERP or CRM software? If you want both, then you can either have software run separately or add CRM to ERP. When it comes to cloud CRM vs. Cloud ERP, you should know the best option based on your needs and financial ability. As a small business, you should probably postpone ERP installation and implement the cheaper cloud CRM. As a medium-size or large-scale business, you should either integrate ERP and CRM or run each software tool separately. Considering all things, running an ERP on the cloud will be more beneficial because it includes several business functions.
Conclusion
So far, you know the difference between CRM and ERP systems and the similarities as well. You also understand that you can either use an ERP system with a CRM module or use CRM independently. If you are a distributor, you can have ERP with supply chain management and customer relationship management modules. What you require to succeed is an ERP CRM consultant to help you select and install the best software for your organization.
Related articles
- What is ERP? | How It Can Help Your Business Grow
- How to Choose an ERP Consultant?
- ERP for Distributors – Warehouse Management Software
- 6 Key Benefits of ERP Accounting System
- Best Purchase Management ERP | Top Order ERP Systems
- 8 Features that Describe the Importance of ERP for Business
- What is Cloud ERP and How Does It Work? | Advantages of Cloud ERP
Posted on
What is an ERP Platform?
A corporate ERP Platform Software is broader than any standalone business management software. It is a merger of different software tools used for running a business. Thus, an ERP Platform Software has other software modules, including accounting, warehousing, distribution, purchasing, inventory management, finance, payroll, sales and marketing, and supply chain. Depending on your business size and type, you can have as many modules as you like.
The best ERP Platform software is customizable. So, you can add extra modules and features to it to ensure it meets all your business needs. The first ERP was developed in the 1960s, and in 1972, SAP made its first automated system. From the 1990s to 2021, the Software has mainly evolved, and many businesses have adopted it. Now ERP is on the cloud. ERP Platforms such as the Ximple Cloud ERP platform for wholesale distributors provide a unique competitive advantage by offering core distribution wholesale industry functionalities while offering open APIs and microservices to integrate with other systems with ease.

A corporate ERP system is broader than any standalone business management software. It is a merger of different software tools used for running a business. Thus, an ERP Platform has other software modules, including accounting, finance, payroll, sales and marketing, warehousing, CRM, and supply chain. Depending on your business size and type, you can have as many modules as you like.

The best enterprise resource management software is customizable. So you can add extra modules and features to it to ensure it meets all your business needs. The first ERP was developed in the 1960s, and in 1972, SAP made its first automated system. From the 1990s to 2021, the Software has mainly evolved, and many businesses have adopted it. Now ERP is on the cloud.
Table of Contents
- What is Cloud Computing Platforms for ERP applications?
- Open Source ERP Platforms
- ERP Software Platform Features
- ERP Platform Benefits
- ERP Platforms Challenges
- Small to Large Size Wholesale Distributors: Selection of ERP Platforms
- Global Wholesale Distributors: Selecting ERP Platforms
- Implementing ERP
What are Cloud Computing Platforms for ERP applications?
An ERP on a cloud platform refers to a system that is accessible on the internet anytime and anywhere. It is typically hosted online by the software provider, and they can offer it as a service you can purchase every month; it is primarily SaaS-based. A business requires a connection to the host’s web server.
A cloud-based platform provides real-time insights to all involved in the running of a business. All cloud ERPs offer core business functions plus others. It is hard to find an ERP software platform that does not have these modules:
- Finance and accounting.
- Human Capital Management
- Customer Relationship Management.
- Inventory Management.
- Warehouse Management System (WMS).
- Supply Chain Management.
- Order Management.
- Procurement.
- Project Management.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
Many benefits follow when the wholesale distribution business implements cloud enterprise resource planning solutions. The immediate ones are that a software provider will manage the application totally from their end. They will make sure your application is hosted 24/7 and produce real-time security updates and feature upgrades. On-premise ERP software requires a business to use its skilled employee to maintain and upgrades the system.
Open Source ERP Platforms
These platforms are offered for free. They are the best when you want to use ERP business software but don’t have the capital to implement it. Software like SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics are not for everyone. They are fantastic but too pricey for some upcoming businesses to afford. Ximple Cloud-based ERP is an excellent alternative to those companies if you are in the wholesale distribution business exploring Next Generation ERP software. Many companies need to use open-source ERPs if they do not have a software budget. Though they cannot offer all the features found in premium products, open-source options are better than none at all.
As most of these are downloadable web applications, anyone can use them. But, there should be a server to which you will install your open-source ERP platform. Support will come from either the active user community or an outsourced entity.
A list of Technologies for ERP Platforms
The following is a list of technologies that developers use in their ERP-based Software.
Options for databases include:
- Oracle SQL
- MSSQL
- PostgreSQL
- IBM DB2
Programming Options:
- Python
- PHP
- Java
- Ruby
- NET and ASP.NET.
Options for Frontend:
- Vue.JS
- JavaScript
- React
- AngularJS.
- PHP Frontend
ERP Software Platform Features
An ERP computer system should have certain features to perform well. A primary platform should at least offer the most critical business management modules. These are:
Accounting and finance
This module should support primary accounting roles like bookkeeping, cost accounting, and financial accounting. Thus, it needs to have Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, and a General Ledger. This module will be crucial to your accountant and financial analyst.
Human Capital Management module
This is all about the management of all expenditures that your workers generate. It should simplify your payroll issues.
This will depend on the kind of business you do. If you are a distributor, it is apparent that you run a warehouse. This module will simplify all warehousing activities.
Customer Relationship Management module
Without customers, any business is nothing. Thus, the best discreet ERP platform should have a module that can help customers track their shipments.
This module helps with stock management. When an item is out of stock, the Software can reorder it automatically.
Other modules you can add based on the business you run and its size include:
Sales and orders management
Compliance Management
Supply Chain Management
Marketing Management
Project Management
This module should support primary accounting roles like bookkeeping, cost accounting, and financial accounting. Thus, it needs to have Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable, and a General Ledger. This module will be crucial to your accountant and financial analyst.
ERP Platform Benefits
We have told you what ERP and ERP solutions are all about. Now you need to know the benefits of implementing these solutions. These include:
- High-quality customer care service and relationships because customers can now track their shipments live and leave feedback.
- A simplified business management role because all business processes are centralized and can be tracked and managed at once.
- Cloud-based ERPs lead to optimal business performance because users don’t have to be stuck in an office to access them. They only need their mobile internet device to see the status of the business processes they are responsible for.
- Human errors are significantly reduced, which boosts the productivity of the business and saves time. Time is a resource you can use where it is needed the most.
- Information is right in front of everyone using the Software. This can enhance communication and collaboration between employees and their managers.
- Enterprise resource planning ERP software leads to lower operating costs as it renders some human tasks redundant and not worth paying for.
ERP Platforms Challenges
Although the electronic resource planning tool sounds great, it’s not easy to implement. The main challenge that affects small and medium enterprises is the initial cost being too high. Other than that, businesses looking to implement this platform may experience these challenges:
- There are several phases during the implementation process, and each has a critical role. One sloppy action in a phase can destroy everything. Thus, forming an expert project management team is a challenge.
- The original implementation budget may fail to include essential software capabilities or features. If these are discovered late in the process, it can be expensive to add them.
- Gathering all data sources from various departmental records that need to be shifted to the new ERP computer system is complicated.
- Duplicated data errors can be a challenge when moving your older software systems’ information to the new Enterprise Resource Planning tool.
- Managing resistance to change among employees is a challenge as some of them may be reluctant to learn.
- If a business has an on-premise ERP platform, it can find it hard to do continuous software upgrades.
Small to Large Size Wholesale Distributors: Selection of ERP Platforms
Small, medium, and large-scale wholesalers still run various departments. Even those small enough to have an office for every business function must take care of finance, accounting, sales and marketing, procurement and purchasing, warehousing, inventory management, and so on. So they need ERP for enterprises to simplify each business function and increase their profitability.
As a small business, you should select an affordable, scalable, and user-friendly ERP. Whether it is bought or open-source Software, make sure it meets the needs of your small business. Medium and large-size businesses may have adequate capital to roll out the ERP software. They should focus on selecting the best software provider to avoid wasting time and money. This should be a stable software producer that can also provide periodic security updates and new software packages to upgrade.
Global Wholesale Distributors: Selecting ERP Platforms
Some wholesale distribution businesses begin small in one country. Due to upward growth, they moved to the neighboring nations and at last shifted operations to many countries worldwide. If you are running such a wholesale business, then one critical tool you need is a distribution ERP platform. You should assess it properly by first determining the features required by your company.
As yours is a multinational wholesale business, you need several business management modules in an all-ERP platform. To determine all the required features, you might have to consult a software provider directly. Some can offer a free analysis to assist you in creating a sensible budget plan.
Implementing ERP
Once you have decided on the ERP product you want to buy, the next step will be selecting ERP platform components and implementing them. The deployment process is usually long and complex, explaining why businesses need to choose one implementation approach that could work for them. Some decide to roll out the platform all at once, while others decide to do it in phases.
Other decisions that should be made concern the type of deployment process that best suits the company. Will it be cloud-based or on-premise? If you choose cloud-based, you will have to select among Software as a Service (SaaS), open-source cloud, or a privately hosted cloud service that you host or hosted by a designated entity.
FAQ
What is ERP, and how does it work?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a multi-functional business management software tool. It consists of many modules, including accounting/finance, procurement, warehousing management, inventory management, human capital management, etc.
ERP modules for a company depend on its size, processes, and industry. For instance, a manufacturing company may need an ERP with project management, accounting, customer relationship management, inventory management, and professional services automation.
An ERP has a central data repository for storing real-time data. As a result, it provides better visibility across departments. Any authorized party seeking the truth can get insights from the central database.
How much does an ERP cost?
ERP cost does not just include the actual software purchase price. In addition, you must factor in the maintenance fees, the implementation cost, ongoing training cost, and software support cost. Working closely with an ERP vendor can help you distinguish various ERP costs. Also, some vendors will quote a price and expose hidden fees later.
Working with a reputable ERP vendor is imperative. Legacy ERP systems are costlier than cloud ERPs because they need to be in your office. Cloud ERPs stay in an online server, making them accessible anywhere. Moreover, cloud ERP vendors incur maintenance and upgrading costs while users meet subscription rates.
How to implement an ERP system?
ERP implementation is a technical exercise requiring adequate preparation. After finishing the long ERP selection process, your team should take the time to start the implementation process. Companies implement ERP in phases to end up with the desired result. No matter what, those spearheading the operation should do the following:
- Involve all users – Every person who will use the new ERP systems should be part of its implementation procedure. This is an effective way of avoiding resistance to change and boosting software acceptance.
- Understand the business goals – Each company has strategic goals it can achieve faster with ERP software. Before implementing ERP, a business should know what it wants from the software.
- Determine the project timeline – An ERP implementation process will take time to end. All in all, your team should estimate the correct deadline. As the team needs adequate time for training users and testing the system, choose an extended deadline.
What is an example of an ERP system?
- Netsuite – This ERP is a comprehensive system based on the cloud. It is ideal for managing all your business management tasks, including inventory, warehousing, accounting/finance, sales order, procurement, customer relations, etc. It is among the best software tools for automating your entire supply chain as it provides real-time visibility. Netsuite will automatically compute your stock levels and other affairs even if you have many branches.
- Microsoft Dynamics – Microsoft Corporation is the provider of Microsoft Dynamics software. There are ERP options for small and medium enterprises, including NAV, SL, and NAV. Their AX software is the primary choice for enterprises. No matter your preference, Microsoft Dynamics will drive performance with its AI-based tools, boost operational efficiency, and make your business more agile.
- Ximple solution (wholesale distributors) – This is your ultimate ERP solution if you are a wholesale distributor. It spans different industries and enables you to run all your business channels with one license. It has all the necessary modules you need depending on your industry. Whether you want to shift to a more capable ERP system or need to invest in this for the first time, Ximple Solution is the best SaaS-based platform.
You can also choose Hybrid, which provides a wide range of deployment and hosting options. On-premise EPR implementation is a good choice when you want to place Software onto your server and run it personally. It is not even closer to having the benefits that a cloud-based platform ERP system can give you.